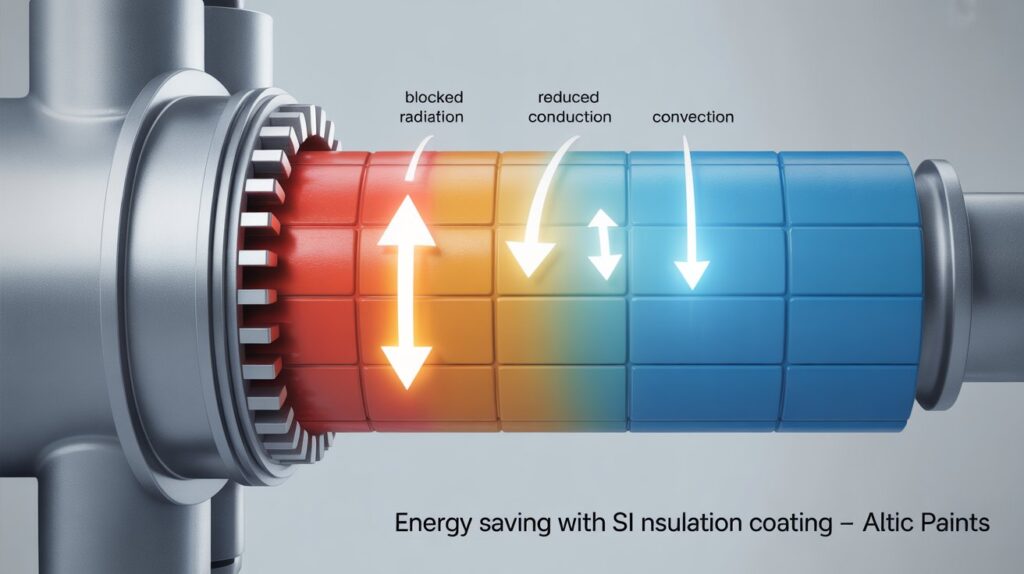
In an era where energy conservation, comfort, and sustainable technology are trending topics, finding smart ways to reduce heat loss is essential for homes, businesses, and industry. One of the most promising solutions is insulation coatings like Altic Paints' SI Insulation Coating. But what makes this coating special, and how does it target all three major modes of heat transfer: radiation, conduction, and convection? Let's take a deep dive—layer by layer.
Understanding the Three Modes of Heat Loss
Before exploring how SI Insulation Coating works, let’s clarify the science of heat transfer:
- Radiation – Heat is emitted in the form of electromagnetic waves (primarily infrared). Even in a vacuum, heat can escape this way—think of the warmth radiating from the sun or a hot boiler.
- Conduction – Heat moves through solids from a hot region to a cooler one. If you touch a metal roof baking in the sun, you feel conduction first-hand.
- Convection – Heat transfer via fluids (air or liquids) moving due to temperature differences. Warm air rising off a roof or hot pipeline is convection in action.
Why Traditional Insulation Methods Often Fall Short
- Bulk insulation (like fiberglass or foam) usually targets conduction.
- Reflective foils may reduce radiation, but only when properly installed and pristine. Over time, dust and damage can ruin their effectiveness.
- Few solutions effectively address all three types of heat loss—and keep working in real-world conditions.
What Makes Altic Paints’ SI Insulation Coating Unique?
Altic Paints’ SI Insulation Coating is a high-performance, elastomeric, and ceramic-based coating designed for roofs, walls, industrial tanks, pipelines, and much more. Its advanced formulation provides a triple-action barrier, dramatically reducing heat flow from all three transfer modes.
1. Battling Radiation: Reflecting and Scattering Heat
- High Solar Reflectance: The coating uses advanced ceramic microspheres and pigments that scatter and reflect solar and infrared radiation back to the environment, minimizing absorption by the underlying surface.
- Up to 85% total reflectance is reported for similar coatings.
- Thermal Emittance: Some of the heat that does get absorbed is radiated back, thanks to the coating’s high thermal emittance properties.
- Durability: Unlike metal foils or ordinary white paints, these properties don’t degrade quickly, even when exposed to dust, rain, or UV.
2. Stopping Conduction: Creating a Poor Heat Pathway
- Low Thermal Conductivity: The SI Coating forms a dense, micro-porous layer once dried. Materials like hollow glass or ceramic microspheres have extremely low thermal conductivities—sometimes lower than air itself.
- Physical Barrier: The continuous film fills cracks, bridges surface imperfections, and creates a uniform layer that poorly conducts heat, whether applied to metal, concrete, or masonry.
- Polymeric Flexibility: The elastomeric matrix means it can expand and contract with the substrate without cracking, maintaining insulation integrity for years.
3. Halting Convection: Sealing Against Airflow
- Waterproof and Airtight Layer: The liquid-applied coating hardens to a seamless, flexible film, preventing air (and moisture) movement across the surface—reducing convective losses.
- Weatherproofing: It also blocks outside moisture and air infiltration, preventing heat or cooling “leaks” from the structure beneath.
Scientific Foundation: Why This Works
- Composite Construction: SI Insulation Coating is a composite—ceramic or glass microspheres (for blocking heat) suspended in an acrylic or elastomeric resin (for flexibility, adhesion, and durability).
- Closed Pore Structure: Advanced formulations may incorporate both closed and open porosity. Closed-cell microspheres trap tiny pockets of air, further lowering conduction and making it nearly impossible for convection within the coating layer.
- Hydrophobic (Water Repellent): By excluding water, the coating’s insulating properties are preserved in humid or rainy environments.
Real-World Applications and Benefits
Industrial Use Cases
- Tanks, Boilers & Pipes: Prevent heat loss, reduce risk of burns or injury, and cut energy costs in factories and refineries.
- Roofs & Walls: Dramatically reduce heat ingress in summer and loss in winter, cutting HVAC costs and improving interior comfort.
Secondary Benefits
- Anti-Corrosive & Protective: Many SI coatings inhibit rust and corrosion.
- Fire Resistance: Some variants add fire-retardant properties for extra safety.
- Eco-Friendly & Cost-Effective: Reduced energy use lowers carbon footprint and energy bills.
- Longevity: Elastomeric, weatherproof formulation resists UV, dirt, and rain, maintaining performance for years with little maintenance.
Altic Paints SI Insulation at a Glance
| Feature | Impact |
| High Solar Reflectivity | Blocks 70–90% solar heat gain |
| Low Thermal Conductivity | Slows direct heat flow through the substrate |
| Seamless, Airtight Barrier | Stops air/moisture transfer, prevents convection |
| Elastomeric, Durable Film | No cracking or peeling, even in harsh climates |
| Multi-Surface Application | Metal, concrete, masonry, bituminous, more |
| Waterproof & Anti-rust | Extra protection for longevity |
Expert Comments: What the Science Says
“Most conventional insulation only addresses bulk heat transfer. Smart coatings like Altic’s SI use micro-engineered materials to control heat flow at the surface, where the biggest losses begin. By combining reflection, low conductivity, and airtightness, you attack all modes of heat loss simultaneously.”

Latest Trends & Why This Matters Now
- Climate Adaptation: With rising temperatures and more extreme weather, keeping buildings cool and protected is now a priority for cities and industries.
- Decarbonization: Cutting energy waste is a top tactic for green building certification and carbon emission reduction.
- Smart Retrofit: Unlike bulky insulation, coatings can be easily applied to existing structures—without major renovation.
Case Study: How SI Insulation Changed the Game
A manufacturing plant in Vadodara applied SI Insulation Coating to its metal-roofed warehouses. After application, the company noted:
- A measured surface temperature drop of up to 20°C on hot days.
- Lower air conditioning bills by 20–30% during summer months.
- Less thermal shock and expansion, reducing roof maintenance costs.
Step-by-Step Application Guide (Quick Overview)
- Surface Prep: Clean and dry the substrate. Remove rust, dust, or old loose paint.
- Primer (if needed): Apply a suitable primer for excellent adhesion.
- Coating Application: Spray or brush on the SI Insulation Coating as per manufacturer guidelines. Usually 2–3 coats achieve best results.
- Curing: Allow the coating to dry and cure fully for maximum performance.
FAQs: Concise Answers to Trending Questions
- How thick should the SI insulation layer be?
- Usually between 0.5 mm and 2 mm, depending on performance goals and substrate.
- Is it suitable for exterior and interior use?
- Yes. It withstands sun, wind, rain, and temperature extremes, as well as indoor climates.
- Does it affect the look of my building?
- Available in various colors or plain white for maximum reflectivity.
- How is it different from regular paint?
- Regular paint offers little or no insulation. SI Insulation Coating is engineered with specialized fillers and resin systems to reduce all modes of heat loss.
Summary: SI Insulation Coating by Altic Paints
- Targets all key modes of heat transfer: radiation, conduction, and convection.
- Backed by material science: engineered microspheres, low-conductivity matrix, and a seamless barrier.
- Delivers energy savings, comfort, and equipment protection.
If you're looking for a modern, trending solution to keep your home or facility cool, safe, and energy-efficient—without the hassle of bulky, traditional insulation—Altic Paints' SI Insulation Coating could be the game-changer you've been waiting for.