Introduction to Heat Resistant Paint
Heat resistant paint is specially formulated to withstand extreme temperatures, prevent corrosion, and extend the lifespan of metal surfaces and industrial equipment. Unlike regular paint, it maintains integrity under thermal stress, making it essential for ovens, chimneys, engines, and heavy machinery.
What Is Heat Resistant Paint?
Heat resistant paint is a coating designed to endure high temperatures without degrading. It forms a protective layer that prevents oxidation, rust, and thermal damage, keeping metal surfaces strong and safe.
How It Differs from Regular Paint
Why Heat Resistance Matters for Metals and Industrial Equipment
The Science Behind Heat Resistant Paint
Heat resistant paint is engineered using advanced material science to survive extreme temperatures while protecting metal surfaces. Unlike conventional coatings, it maintains structural integrity, adhesion, and performance even under continuous thermal stress.
Thermal Stability and Heat Reflection
Thermal stability refers to a coating’s ability to remain intact without cracking, peeling, or softening when exposed to high temperatures. Heat resistant paints achieve this through:
By reflecting heat instead of absorbing it, these coatings help lower surface temperatures and protect the underlying metal from thermal fatigue.
Chemical Composition That Withstands High Temperatures
The performance of heat resistant paint depends on its specialized formulation, which typically includes:
These components work together to ensure the coating remains chemically stable even at temperatures exceeding 600°C, making it ideal for furnaces, exhaust systems, boilers, and industrial equipment.
How Coatings Prevent Oxidation and Corrosion
At high temperatures, metals are highly vulnerable to oxidation and corrosion. Heat resistant coatings protect surfaces by:
This protective action not only preserves the metal’s strength but also extends equipment lifespan and reduces maintenance costs, especially in harsh industrial environments.
Applications of Heat Resistant Paint
Heat resistant paint is widely used across industrial, commercial, automotive, and household sectors where surfaces are exposed to extreme temperatures. These coatings protect substrates from heat damage, corrosion, and premature failure while maintaining performance and appearance.
Heat Resistant Paint for Metal Surfaces
Metal surfaces are highly vulnerable to thermal expansion, oxidation, and corrosion when exposed to heat. Heat resistant paint for metal creates a durable protective layer that:
It is commonly applied to steel structures, pipelines, chimneys, exhaust ducts, and storage tanks in industrial environments.
Use in Industrial Equipment and Machinery
Industrial machinery operates under constant thermal stress. Heat resistant coatings play a critical role in:
These coatings ensure long-term protection even in aggressive environments involving heat, chemicals, and moisture.
Household Applications: Stoves, Fireplaces, and BBQs
Heat resistant paint is also essential in residential settings where high temperatures are common. Typical household applications include:
The coating prevents discoloration, cracking, and surface degradation while improving both safety and aesthetic appeal.
Automotive and Aerospace Uses
In the automotive and aerospace industries, heat resistant paint is critical for components exposed to extreme temperatures, such as:
These coatings offer thermal protection, oxidation resistance, and long-lasting durability, helping critical components perform reliably under severe operating conditions.
Key Benefits of Using Heat Resistant Paint
Heat resistant paint offers more than just temperature tolerance. It provides long-term protection, safety, and cost efficiency for metal surfaces and equipment exposed to extreme heat in industrial, commercial, and residential environments.
Protects Surfaces from Extreme Heat Damage
High temperatures can cause ordinary coatings to blister, crack, or peel. Heat resistant paint is specifically formulated to:
This protection ensures surfaces remain stable even under intense heat exposure.
Prevents Rust, Corrosion, and Weathering
When metals are exposed to heat, moisture, and oxygen, corrosion accelerates. Heat resistant paint forms a durable protective barrier that:
This makes it ideal for both indoor and outdoor high-temperature environments.
Enhances Longevity of Equipment and Structures
By minimizing heat-related damage and corrosion, heat resistant coatings significantly extend the service life of equipment and structures. Benefits include:
This makes heat resistant paint a cost-effective investment for industries.
Improves Safety in High-Temperature Environments
Safety is a critical concern in high-heat applications. Heat resistant paint contributes to safer operations by:
This added layer of protection helps ensure compliance with safety standards and protects personnel and property.
Types of Heat Resistant Paint
Heat resistant paints are available in different formulations, each designed to perform under specific temperature ranges and operating conditions. Choosing the right type depends on the level of heat exposure, surface material, and application environment.
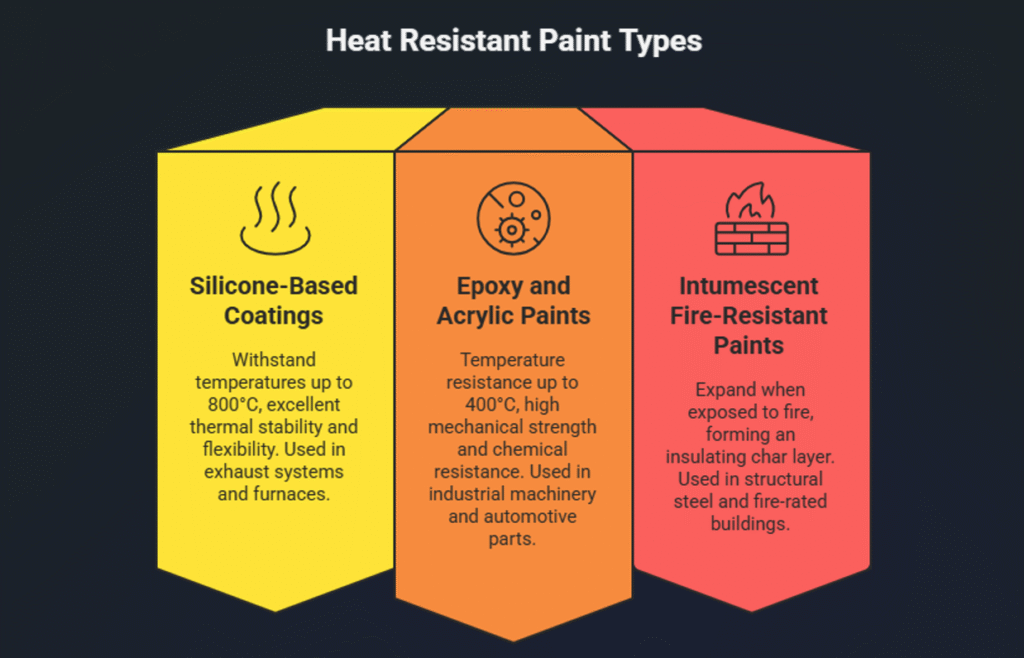
Silicone-Based Coatings
Silicone-based heat resistant paints are among the most commonly used coatings for high-temperature applications. They offer excellent thermal stability and flexibility.
Key features:
Common applications:
Exhaust systems, chimneys, furnaces, boilers, and industrial pipelines.
Epoxy and Acrylic High-Temperature Paints
Epoxy and acrylic heat resistant paints are designed for moderate to high-temperature environments where durability and chemical resistance are also required.
Key features:
Common applications:
Industrial machinery, processing equipment, automotive parts, and metal structures exposed to intermittent heat.
Intumescent Fire-Resistant Paints
Intumescent coatings are a specialized type of heat and fire-resistant paint designed primarily for fire protection rather than continuous heat exposure.
How they work:
Key benefits:
Common applications:
Structural steel, fire-rated buildings, industrial plants, and commercial facilities.
How to Apply Heat Resistant Paint Effectively
Proper application is essential to achieve maximum performance from heat resistant paint. Correct surface preparation, suitable tools, and proper curing ensure long-lasting protection and heat resistance.
Surface Preparation Tips
Surface preparation is the most critical step before applying heat resistant paint. A poorly prepared surface can lead to peeling, blistering, or coating failure.
Best practices include:
Proper preparation improves adhesion and enhances the coating’s heat resistance performance.
Recommended Tools and Techniques
Heat resistant paint can be applied using different methods depending on the project size and surface condition.
Common application tools:
Application tips:
Using the right technique ensures a smooth finish and optimal thermal performance.
Curing and Drying Guidelines
Curing is essential for activating the heat-resistant properties of the coating.
Key curing guidelines:
Proper curing helps the coating achieve maximum hardness, adhesion, and long-term durability under high-temperature conditions.
Conclusion: Why Heat Resistant Paint Is a Smart Investment
Heat resistant paint is more than just a protective coating—it is a long-term solution for safeguarding metal surfaces and equipment exposed to high temperatures. By withstanding extreme heat, preventing corrosion, and maintaining structural integrity, these specialized coatings help reduce damage caused by thermal stress and harsh operating conditions.
Investing in heat resistant paint improves the lifespan of industrial equipment, metal structures, and household appliances while lowering maintenance and replacement costs. It also enhances safety by preventing coating failure, oxidation, and potential fire hazards in high-temperature environments. Whether used in industrial machinery, automotive components, or household applications, heat resistant paint delivers durability, efficiency, and reliable performance.
For industries and users looking to protect valuable assets and ensure long-term operational safety, heat resistant paint is a smart, cost-effective investment that delivers lasting protection and peace of mind.


as soon as I found this site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.