Heat resistant paints are specially formulated coatings designed to protect surfaces exposed to high temperatures. These paints play a critical role in preventing damage such as cracking, peeling, corrosion, and discoloration when substrates face continuous or intermittent heat. Commonly used on industrial equipment, chimneys, exhaust systems, furnaces, boilers, and metal structures, heat resistant paints ensure both safety and durability.
There are several types of heat resistant paints based on composition and performance. Silicone-based heat resistant paints are widely used due to their excellent thermal stability and resistance up to 600–650°C. Epoxy heat resistant coatings offer strong adhesion and chemical resistance, making them suitable for moderate temperature applications. Ceramic-based heat resistant paints provide superior insulation and can withstand extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C. Additionally, intumescent and specialty heat coatings are used where fire protection and thermal expansion control are required.
Choosing the right heat resistant paint depends on operating temperature, surface material, and environmental exposure, ensuring long-lasting high-temperature protection.
Introduction to Heat Resistant Paints
What Are Heat Resistant Paints?
Why Standard Paints Fail at High Temperatures
Importance of High-Temperature Coatings in Industrial & Domestic Use
Understanding How Heat Resistant Paints Work
Heat Resistance vs Fire Resistance
Heat resistant paints are made to handle continuous high temperatures without breaking down. They protect surfaces from heat damage during normal operations. Fire resistant paints, on the other hand, are designed to slow down the spread of fire and provide escape time during emergencies. Both serve different purposes and should be chosen based on application needs.
Role of Resins, Binders, and Pigments
The performance of heat resistant paint depends on its formulation. Special resins like silicone help the coating stay stable under extreme heat. Strong binders ensure the paint remains firmly attached, while heat-stable pigments prevent fading, burning, or discoloration.
Thermal Barrier and Insulation Properties
Heat resistant paints create a protective barrier between the surface and high temperatures. This layer reduces heat transfer, protects the substrate, and helps prevent cracking, corrosion, and long-term structural damage.
Major Types of Heat Resistant Paints
Silicone-Based Heat Resistant Paints
Temperature Range
Silicone-based paints can typically withstand temperatures ranging from 200°C to 650°C, making them ideal for continuous heat exposure.
Key Features & Benefits
These coatings offer excellent thermal stability, resistance to cracking, and long-lasting color retention. They also provide good corrosion protection on metal surfaces.
Typical Applications
Commonly used on exhaust systems, chimneys, furnaces, boilers, and industrial pipelines.
Epoxy Heat Resistant Coatings
Heat Tolerance Limits
Epoxy heat resistant coatings generally perform well up to 150°C to 250°C, depending on formulation.
Mechanical Strength & Adhesion
They are known for strong adhesion, high mechanical strength, and excellent chemical resistance.
Industrial Usage
Widely used in industrial floors, equipment, tanks, and areas exposed to heat along with chemicals or abrasion.
Polyurethane Heat Resistant Paints
Flexibility & Finish Quality
Polyurethane coatings provide a smooth, decorative finish with good flexibility, helping resist minor surface movement.
Moderate Heat Resistance
They can typically withstand temperatures up to 120°C to 150°C, suitable for moderate heat conditions.
Automotive and Architectural Use
Commonly applied in automotive components, exterior structures, and architectural metal surfaces.
Ceramic-Based Heat Resistant Coatings
Extreme Temperature Resistance
Ceramic coatings are designed to handle extremely high temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C.
Thermal Insulation Performance
They offer superior insulation by reflecting heat and reducing thermal transfer to the substrate.
Heavy-Duty Industrial Applications
Used in furnaces, kilns, power plants, petrochemical units, and high-temperature processing equipment.
Intumescent Heat Resistant / Fireproof Paints
Fire-Reactive Coating Mechanism
When exposed to fire, intumescent coatings expand to form a thick, insulating char layer.
Passive Fire Protection Role
This char layer slows heat transfer, protecting structural integrity and allowing evacuation time.
Structural Steel and Fire Safety Uses
Commonly used on structural steel, fire doors, commercial buildings, and critical fire safety applications.
Heat Resistant Paints by Application
Industrial Heat Resistant Paints
Boilers, Furnaces, Reactors
Industrial heat resistant paints are designed to withstand continuous high temperatures and harsh operating conditions. They protect boilers, furnaces, and reactors from thermal damage, oxidation, and corrosion, ensuring longer equipment life and safe performance in demanding industrial environments.
Automotive & Exhaust System Coatings
Exhausts, Manifolds, Engine Parts
These coatings are specially formulated to handle extreme heat generated by engines and exhaust systems. They prevent rust, reduce heat damage, and maintain performance on exhaust pipes, manifolds, and other high-temperature automotive components.
Residential & Commercial Applications
Fireplaces, Chimneys, BBQ Grills
In residential and commercial settings, heat resistant paints are used on fireplaces, chimneys, and BBQ grills. They improve safety, enhance appearance, and protect surfaces from heat exposure, discoloration, and wear over time.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing Heat Resistant Paint
Maximum Service Temperature
Always check the maximum temperature the paint can withstand. The coating should safely handle continuous and peak heat without cracking or failing.
Adhesion at Elevated Temperatures
Good heat resistant paint maintains strong bonding even under thermal expansion, preventing peeling, blistering, or flaking over time.
Corrosion & Chemical Resistance
In industrial and outdoor environments, the paint must resist corrosion, moisture, oils, and chemicals to ensure long-term protection.
UV & Weather Stability
For exterior applications, UV resistance and weather stability are essential to prevent fading, chalking, and surface degradation.
Indoor vs Outdoor Suitability
Choose formulations specifically designed for indoor or outdoor use, considering exposure to heat, moisture, sunlight, and environmental conditions.
Comparison Table – Types of Heat Resistant Paints
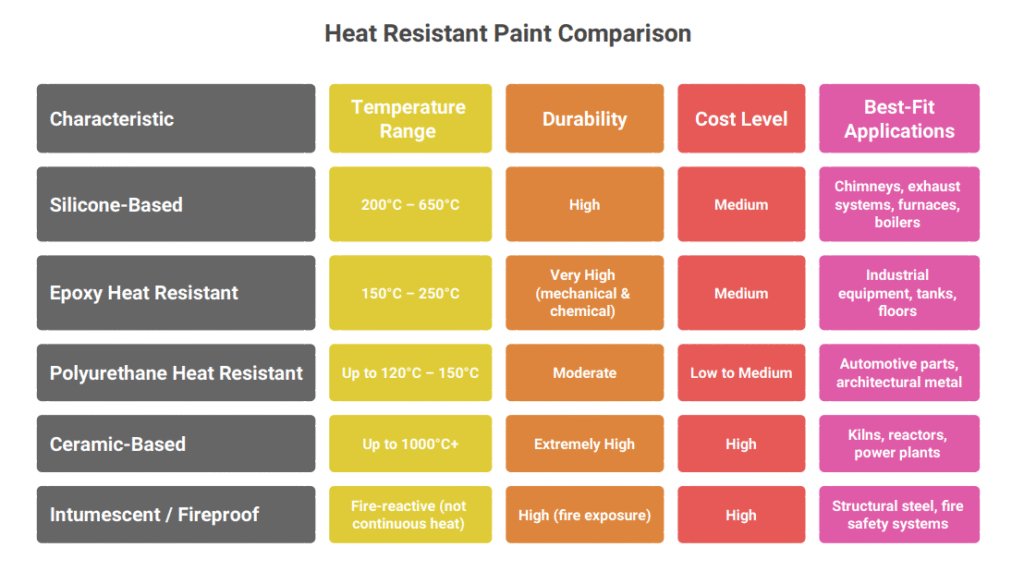
This comparison helps in selecting the right heat resistant paint based on temperature exposure, durability needs, budget, and application requirements.
Application & Maintenance Best Practices
Surface Preparation Guidelines
Proper surface preparation is critical for performance. Surfaces should be clean, dry, and free from oil, grease, rust, and dust. Abrasive blasting or mechanical cleaning is often recommended for metal surfaces to ensure strong adhesion.
Application Methods (Brush, Roller, Spray)
Heat resistant paints can be applied using brush, roller, or spray depending on the area and coating type. Spray application provides the most uniform finish, while brush and roller methods are suitable for small or touch-up jobs.
Curing Process & Heat Cycling
Many heat resistant coatings require a controlled curing process. Gradual heat cycling allows the coating to harden properly and achieve maximum temperature resistance without cracking.
Inspection & Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection helps identify early signs of wear, discoloration, or damage. Timely touch-ups and proper maintenance extend coating life and ensure continuous protection under high-temperature conditions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Choosing the Wrong Temperature Rating
Using a paint that cannot withstand the operating temperature can lead to peeling, cracking, or failure, compromising surface protection.
Skipping Surface Preparation
Applying paint on dirty, oily, or rusty surfaces reduces adhesion and shortens the coating’s lifespan. Proper cleaning and priming are essential.
Improper Curing
Failing to follow the recommended curing process or heat cycling can cause uneven coating, blistering, or poor heat resistance.
Confusing Fireproof vs Heat Resistant Paint
Fireproof (intumescent) paints are designed to delay fire spread, while heat resistant paints protect against high temperatures. Using the wrong type may compromise safety and performance.
How to Select the Right Heat Resistant Paint for Your Project
Industrial vs Residential Needs
Consider the environment and heat exposure. Industrial applications may require high-temperature or ceramic-based coatings, while residential use like fireplaces or grills can use moderate heat-resistant paints.
Cost vs Performance Balance
Higher-performance paints often come at a premium. Balance your budget with the required temperature tolerance, durability, and lifespan to choose the most cost-effective option.
Compliance with Safety Standards
Ensure the selected paint meets relevant safety and environmental regulations, such as fire safety standards, VOC limits, and industrial certifications, to guarantee reliable and compliant performance.
FAQs About Heat Resistant Paints
Is Heat Resistant Paint Fireproof?
Not all heat resistant paints are fireproof. Heat resistant paints protect surfaces from high temperatures, while fireproof (intumescent) paints are designed to slow fire spread and provide passive fire protection.
Can It Be Used Outdoors?
Yes, but you must choose formulations with UV and weather resistance for exterior use. Proper surface preparation and application ensure durability under sunlight, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
How Long Does It Last?
The lifespan depends on temperature exposure, surface type, and environmental conditions. High-quality heat resistant paints typically last 5–10 years under normal operating conditions, with regular inspection and maintenance extending their durability.
Conclusion – Choosing the Right Heat Resistant Paint Matters
Safety, Durability & Long-Term Savings
Selecting the correct heat resistant paint ensures surfaces are protected from thermal damage, extends equipment lifespan, and reduces maintenance costs. Proper coatings prevent cracking, corrosion, and failure, enhancing both safety and efficiency.
Importance of Expert Consultation
Consulting with coating experts helps identify the right type of paint, temperature rating, and application method for your specific project. Expert guidance ensures compliance with safety standards and maximizes performance, providing peace of mind and long-term value.

